Energy crisis: Mega power projects put on back burner as govt changes tack
A $46 billion deal signed with China this year includes several large energy projects
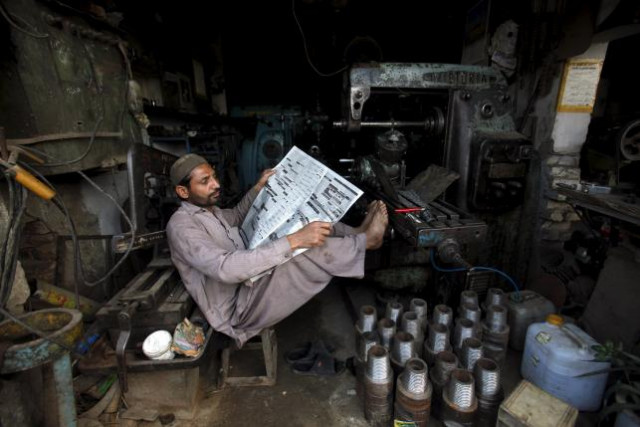

A worker takes a break from his work during a power cut at a workshop on the outskirts of Peshawar, Pakistan, November 5, 2015. PHOTO: REUTERS
Since Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif came to office in 2013, his government announced a string of big-ticket power plants that have failed to live up to their fanfare billing.
A 6,000 megawatt (MW) coal powered park has been quietly put on the back burner. A planned 1,000 MW solar park only has an installed capacity of 100 MW so far, and the Nandipur plant of 425 MW closed days after the prime minister inaugurated it over management and pricing disputes. It recently reopened.
The country produces about 16,000 MW and faces a shortfall of around 6,000 MW, although supply and demand fluctuate, the planning ministry said.
Deadline set: PM vows to end load-shedding by Dec 2017
"They kept hyping generation too much, creating unrealistic deadlines that end in disappointment," said Werner Liepach, Pakistan head of the Asian Development Bank, the biggest external investor in the power sector.
Now, experts say, officials are quietly acknowledging that extra generation alone won't solve power woes, and are beginning to tackle deep-rooted problems like mismanagement, ancient transmission systems and slow privatization.
"Pakistan is making some invisible reforms. If done properly, it should result in a marked improvement in the next one to two years," Liepach said.
Time is pressing, with voters delivering their verdict on Sharif's leadership in 2018 when they go to the polls again.
Energy crisis: 1,320MW project to be competed by 2017: CM
Power cuts have crippled the economy, shaving an estimated two percent off GDP annually, causing unemployment and fuelling public anger in the nuclear-armed nation of 190 million people.
Government promises
Nawaz has made progress in the key sector. Lower oil prices and heavy rains powering hydro projects have helped him slash power shortages by about a third.
On Monday, the government finalised a $16 billion gas import deal with Qatar to import liquefied natural gas, ensuring a more stable energy supply. Pakistan is planning a pipeline and a second terminal that can be extended to Iran once sanctions are lifted.
A $46 billion deal signed with China this year included several large energy projects. Construction has begun on some, while others exist only on paper.
Yet the aging transmission system would collapse if all of the installed generation capacity was being used. It needs urgent upgrades.
The government said it was planning two high-voltage transmission lines and encouraging distribution companies to invest. The lines, capable of carrying up to 4,000 MW each, will cost around $1.2 billion each, the ADB said.
"There was not adequate generation, no adequate investment in transmission and distribution, which led to a bottleneck and a breakdown in governance," said Planning Minister Ahsan Iqbal.
Other reforms include privatising five electricity distribution companies, beginning in March. Most have been criticized for being poorly managed.
FESCO, the distribution company in the industrial hub of Faisalabad, will be the first to be auctioned, with an initial provisional price of around $110 million.
Investors want regulators to reform archaic pricing rules, and are waiting to see progress on a central power purchasing agency that would bring greater transparency to payments.
Payments are currently pooled by the government, penalizing efficient distribution companies who struggle to get powerful consumers to pay bills.
Another problem is unpaid government subsidies that build up until power plant owners cannot afford fuel. The so-called "circular debt" stands at over $3 billion.
Experts say the situation is improving, but some reforms started late due to the "mad scramble" for more generation.
"It's only when things go wrong that they start ... asking for advice," said Jamil Masud, head of electricity consultancy Hagler Bailly Pakistan.
Richard Spencer, lead energy specialist for Pakistan at the World Bank, said Sharif inherited a power system on the brink of collapse. He revived it, but now faced tough political decisions to improve it.
"Much more can be done - much more transparency is needed. There is now, at least ... a plan," said Spencer.


















COMMENTS
Comments are moderated and generally will be posted if they are on-topic and not abusive.
For more information, please see our Comments FAQ