China says Martian rover takes first drive on surface of Red Planet
China this month joined the United States as the only nation to deploy land vehicles on Mars
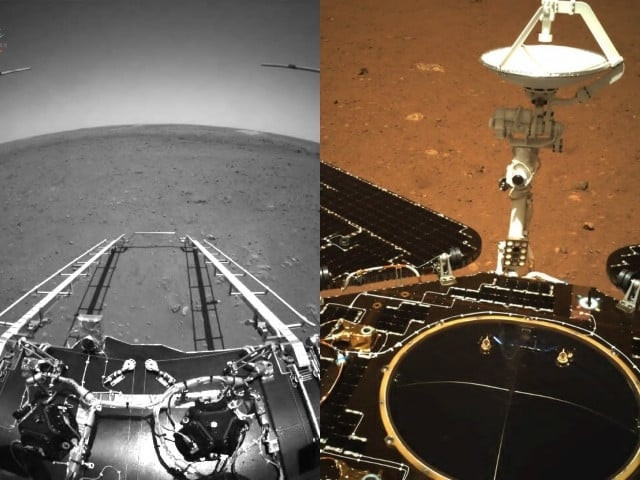
A remote-controlled Chinese motorized rover drove down the ramp of a landing capsule on Saturday and onto the surface of the Red Planet, making China the first nation to orbit, land, and deploy a land vehicle on its inaugural mission to Mars.
Zhurong, named after a mythical Chinese god of fire, drove down to the surface of Mars at 10:40 a.m. Beijing time (0240 GMT), according to a post on the rover's official Chinese social media account.
Here’s how I maneuver. I’ll trundle off the lander in 2-3 days. (HD: https://t.co/zt1lxKVfgV) Major environmental and geological discoveries are expected to be made with scientific payloads as below... #Zhurong #Tianwen1 (1/2) pic.twitter.com/db7zBr6QWG
— Chinese Zhurong Mars Rover (@MarsZhurong) May 19, 2021
China this month joined the United States as the only nation to deploy land vehicles on Mars. The former Soviet Union landed a craft in 1971, but it lost communication seconds later.
China's rover sends back its first 'selfies' from Mars
The 240-kg (530-pound) Zhurong, which has six scientific instruments including a high-resolution topography camera, will study the planet's surface soil and atmosphere.
Powered by solar energy, Zhurong will also look for signs of ancient life, including any subsurface water and ice, using a ground-penetrating radar during its 90-day exploration of the Martian surface.
China's uncrewed Tianwen-1 spacecraft blasted off from the southern Chinese island of Hainan in July last year. After more than six months in transit, Tianwen-1 reached the Red Planet in February where it had been in orbit since.
On May 15, the landing capsule carrying the rover separated from Tianwen-1 and touched down on a vast plain known as Utopia Planitia.
The first images taken by the rover were released by the Chinese space agency on Wednesday.
SpaceX rocketship launches astronauts on NASA mission to space station
Tianwen-1 was one of three probes that reached Mars in February.
US rover Perseverance touched down on Feb. 18 in a huge depression called Jezero Crater, more than 2,000 km (1,240 miles) from Utopia Planitia.
Hope - the third spacecraft to arrive in February - is not designed to land. Launched by the United Arab Emirates, it is orbiting above Mars, gathering data on its weather and atmosphere.
Perseverance and Zhurong are among three robotic rovers operating on Mars. The third is NASA's Curiosity, which landed in 2012.
NASA’s InSight, which arrived on the surface of the planet in 2018 to study its interior, is a stationary module.



















COMMENTS
Comments are moderated and generally will be posted if they are on-topic and not abusive.
For more information, please see our Comments FAQ