Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder affecting millions of women globally. One of the more distressing symptoms is hair loss, which can take a toll both emotionally and physically. In this post, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments for PCOS-related hair loss, as well as home remedies to help manage and prevent further hair thinning.
Causes of PCOS-Related Hair Loss
PCOS causes hormonal imbalances that can disrupt normal body functions. The primary reason for hair loss in women with PCOS is an overproduction of androgens, male hormones that both men and women have. Elevated levels of androgens can lead to hair thinning and even significant hair loss, particularly on the scalp.
Other factors contributing to PCOS-related hair loss include:
- Anovulation (lack of ovulation)
- Inflammation
- Insulin resistance
- Genetics
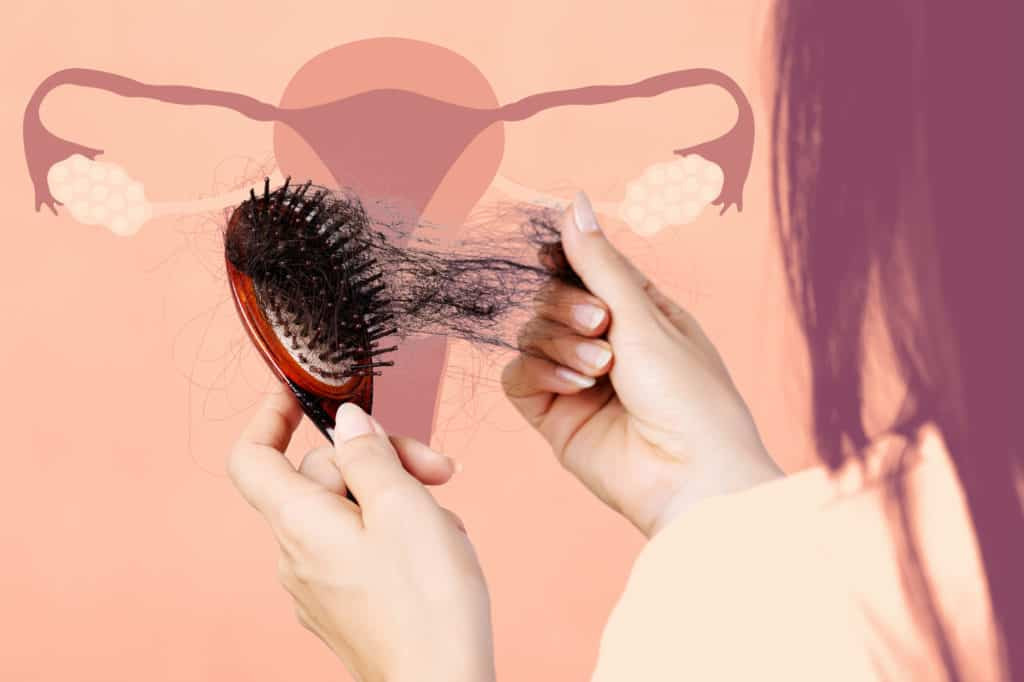

Not every person with PCOS experiences hair loss, and the severity can differ greatly. Treating the root cause of hormonal imbalances and seeking expert advice from dermatologists or endocrinologists can improve symptoms and help regain hair health.
Hormonal Imbalances and Hair Loss
Hormones play a significant role in hair health, and imbalances can lead to various types of hair loss:
- Androgenetic Alopecia: High levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone, can cause hair follicles to shrink, leading to shorter, thinner hair growth and eventual hair loss.
- Telogen Effluvium: Hormonal shifts, such as those from pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can push more hair into a resting phase, leading to shedding.
- PCOS: Elevated androgens can lead to male-pattern baldness or thinning in women.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause abnormal hair shedding and interrupt the hair growth cycle.
- Alopecia Areata: This autoimmune disorder may also be linked to hormonal fluctuations and can cause patches of hair loss.
Treatments for hormonal hair loss include:
- Medications such as hormone regulators or anti-androgens
- Lifestyle changes like diet and exercise to promote hormonal balance
- Topical treatments containing minoxidil or Redensyl to stimulate hair growth
The Role of Insulin Resistance in Hair Loss
Insulin resistance, a hallmark of PCOS, can worsen hair loss. Higher insulin levels may elevate androgens like testosterone, contributing to hair follicle shrinkage. Inflammation caused by insulin resistance may affect scalp health and hair growth.
Managing insulin resistance through a healthy diet and regular exercise may help reduce hair loss.
How to Treat PCOS-Related Hair Loss

If you're experiencing hair loss due to PCOS, there are various treatment methods available:
- Balanced diet: Opt for whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to manage insulin and hormone levels.
- Exercise: Physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and overall hormonal balance.
- Stress management: Yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress, which can worsen hormonal imbalances.
- Consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment options such as medications or supplements.
Hair Care Routines for PCOS Sufferers
Maintaining a good hair care routine can minimize damage caused by PCOS-related hair loss:
- Gentle cleansing: Use mild shampoos that won’t strip your scalp’s natural oils.
- Conditioning: Keep hair hydrated with a conditioner that suits your hair type.
- Avoid heat styling: Minimize the use of hot tools and apply heat protectants when necessary.
- Avoid tight hairstyles: Give your hair follicles a break by opting for looser styles.
Psychological Impact of Hair Loss in PCOS
Hair loss from PCOS can lead to emotional distress, impacting self-esteem and mental health. Many women experience:
- Lowered self-confidence due to changes in appearance
- Anxiety related to social interactions
- Depression from feeling out of control
- Negative body image and social withdrawal
Seeking support through therapy or joining support groups can help manage the psychological toll of hair loss.
Medical Treatment for PCOS-Related Hair Loss
Effective treatment requires addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances. Medical options include:
- Birth control pills to regulate hormone levels
- Spironolactone, an anti-androgen that reduces excess male hormones
- Metformin to manage insulin resistance and potentially reduce hair loss
Consult a healthcare professional to determine which treatment plan is best suited to your needs.
Home Remedies for PCOS-Related Hair Loss
Alongside medical treatment, some natural remedies may help:
- Balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Saw palmetto and green tea supplements to reduce hair loss
- Omega-3 fatty acids to promote healthy hair and scalp
- Scalp massages to increase blood flow to hair follicles
While natural remedies can be beneficial, it's important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider.
Final Thoughts: Treat Your PCOS-Related Hair Loss with Care
PCOS-related hair loss can be challenging, but addressing the root causes and seeking medical advice can make a significant difference. A proper diagnosis is essential to creating an effective treatment plan. With lifestyle changes, medical intervention, and expert guidance, hair regrowth and symptom management are possible.
Symptoms of PCOS-Related Hair Loss
PCOS-related hair loss tends to occur diffusely across the scalp rather than in localized patches. Symptoms include:
- Thinning hair, particularly on the crown
- Excessive shedding
- Changes in hair texture
- Scalp issues like dandruff or dryness
Consulting with a trichologist or dermatologist can help guide you toward effective treatment options.







COMMENTS
Comments are moderated and generally will be posted if they are on-topic and not abusive.
For more information, please see our Comments FAQ