Here’s how social media sites handle world leaders
Facebook’s independent oversight board will announce whether it is overturning the suspension of Trump’s account
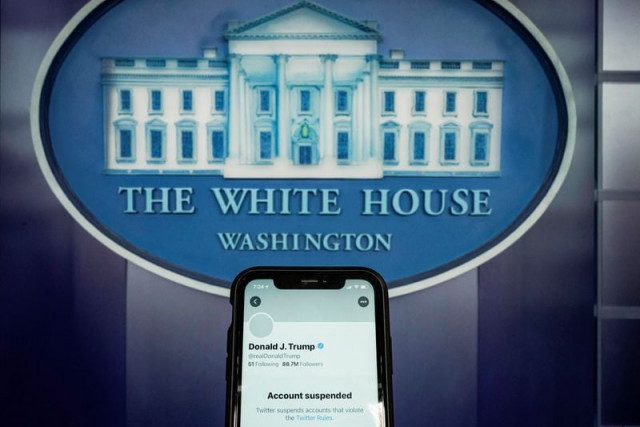
Facebook’s independent oversight board on Wednesday will announce whether it is overturning the company’s suspension of former US President Donald Trump’s account. The long-awaited ruling will bring the focus back onto how the world’s largest social network decides what world leaders and politicians can and can’t say on their platforms.
Here is how big tech companies deal with this thorny issue:
WHO GETS SPECIAL TREATMENT?
Facebook and Twitter currently have rules that give world leaders, elected officials, and political candidates greater latitude than ordinary users.
Facebook defines politicians as candidates running for office, current officeholders, and many cabinet appointees, along with political parties and their leaders. Twitter's public interest rules apply to verified government or elected officials, their appointed successors and candidates, registered political parties, or nominees for public office that have more than 100,000 followers.
WHAT ARE THE CURRENT RULES?
Twitter says it errs on the side of leaving content up when it is in the public interest, including keeping a record to hold leaders accountable. It also allows leaders to interact with other public figures and engage in "foreign policy saber-rattling."
US Supreme Court backs Facebook in case about unwanted texting
In March, Twitter began adding warnings to and restricting the reach of some world leaders' tweets that would be removed if sent by the average user. Twitter also says it pulls world leaders' tweets down for offenses like promoting terrorism or posting private information.
Facebook exempts politicians' posts and paid ads from its third-party fact-checking program, though it did start affixing some separate labels, for example, notices about voter fraud rarity on some of Trump's posts around the election.
The company’s “newsworthiness exemption” also allows politicians’ rule-breaking posts on the site if the public interest outweighs the harm.
Facebook, which had occasionally removed Trump's content for violations like Covid-19 misinformation before he was banned, faced employee backlash for its inaction on inflammatory posts including one during anti-racism protests that said "when the looting starts, the shooting starts."
Alphabet’s YouTube says it does not have different rules for world leaders, though its exception for "educational" or "documentary" content does allow certain news coverage of politicians making rule-breaking statements.
SO WHAT HAPPENED WITH TRUMP?
After the Capitol riot on January 6, Twitter banned Trump for breaking its “glorification of violence” rules, departing somewhat from precedent to take possible interpretations of his tweets into account.
Facebook blocked Trump's accounts on its platforms indefinitely. CEO Mark Zuckerberg said the current context meant the risks of allowing him to use the service were "simply too great."
A slew of online platforms barred the former president, including Snapchat, which had already removed him from its Discover program, and Amazon-owned Twitch, which had previously suspended him for hateful content in June.
PM Imran constitutes committee to review social media rules
YouTube also gave Trump’s channel its first-ever strike following the riot. This would normally come with a week-long suspension but the account remains frozen months later. YouTube CEO Susan Wojcicki said the suspension will be lifted when the company determines the risk of real-world violence has decreased.
WHAT ABOUT OTHER GLOBAL LEADERS?
Human rights groups have argued that tech firms need to apply standards consistently to other global leaders.
Facebook's suspension of Trump followed bans in recent years of some government officials, including in India and Myanmar for promoting violence, but the company had never before blocked a current president, prime minister or head of state.
Leaders who have drawn particular public scrutiny but remain active on social media sites include Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, who has used Twitter to call for Israel’s elimination, and Brazil’s President Jair Bolsonaro, who has posted on Facebook that indigenous citizens were “evolving” and becoming more human.
In March, Facebook put a 30-day freeze on Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro’s page for spreading Covid-19 misinformation. Both Maduro and Bolsonaro have previously had content removed by Facebook and Twitter for this reason during the pandemic.
Earlier this year, Facebook banned the Myanmar military from the site after they took power in a coup. UN human rights investigators have previously said the platform played a key role in fomenting violence in Myanmar.
WHAT'S HAPPENING NOW?
Both Facebook and Twitter have called for input on their rules after facing intense scrutiny over their handling of US presidential election and the storming of the Capitol by pro-Trump supporters.
Facebook has asked its oversight board to give recommendations along with the Trump decision, while Twitter opened a public survey.


















COMMENTS
Comments are moderated and generally will be posted if they are on-topic and not abusive.
For more information, please see our Comments FAQ